Return the root node of a binary search tree that matches the given preorder traversal.
(Recall that a binary search tree is a binary tree where for every node, any descendant of node.left has a value < node.val, and any descendant of node.right has a value > node.val. Also recall that a preorder traversal displays the value of the node first, then traverses node.left, then traverses node.right.)
It’s guaranteed that for the given test cases there is always possible to find a binary search tree with the given requirements.
Example 1:
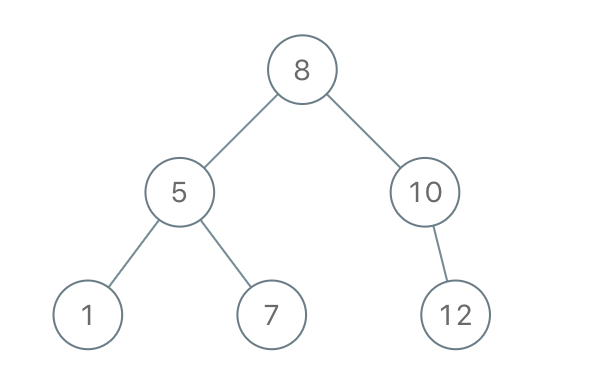
Input: [8,5,1,7,10,12]
Output: [8,5,10,1,7,null,12]
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 1001 <= preorder[i] <= 10^8- The values of
preorderare distinct.
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* bstFromPreorder(vector<int>& preorder) {
return f(preorder, 0, preorder.size() - 1);
}
TreeNode* f(const vector<int>& po, size_t beg, size_t end) {
if (beg > end) return nullptr;
size_t right_beg = beg + 1;
while (right_beg <= end && po[right_beg] < po[beg]) ++right_beg;
return new TreeNode(po[beg], f(po, beg + 1, right_beg - 1), f(po, right_beg, end));
}
};